Dielectrics In Electric Fields Tables Atoms And Molecules: A Comprehensive Guide

Dielectrics are non-conducting materials that possess the unique ability to store electrical energy when subjected to an electric field. Their presence in electrical devices and systems is crucial for controlling the flow of electricity, enhancing performance, and ensuring safety. This article delves into the fascinating world of dielectrics, exploring their properties, behavior in electric fields, atomic and molecular structures, and practical applications.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 85257 KB |
| Print length | : | 796 pages |
Dielectric Properties
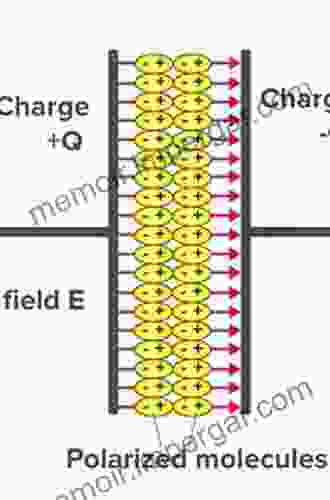
The defining characteristic of a dielectric is its ability to polarize when placed in an electric field. Polarization refers to the alignment of dipoles, which are pairs of opposite charges separated by a small distance. When a dielectric is exposed to an electric field, its constituent dipoles align themselves with the field, creating an internal electric field that opposes the external field. This phenomenon is known as dielectric polarization.
The degree of polarization in a dielectric is quantified by its permittivity or dielectric constant. Permittivity represents the ability of a material to store electrical energy and is measured relative to the permittivity of vacuum. Dielectric materials with high permittivity store more electrical energy for a given electric field strength.
Behavior in Electric Fields
When a dielectric is subjected to an electric field, it experiences several distinct effects. The primary effect is dielectric polarization, as discussed earlier. Additionally, dielectrics can exhibit phenomena such as dielectric displacement and dielectric relaxation.
Dielectric displacement refers to the shift of charges within a dielectric under the influence of an electric field. This displacement creates an internal electric field that opposes the external field, effectively reducing the net electric field within the dielectric.
Dielectric relaxation, on the other hand, describes the time-dependent response of a dielectric to a changing electric field. When an electric field is applied to a dielectric, it takes some time for the dipoles to align with the field, resulting in a gradual increase in polarization. Similarly, when the electric field is removed, the dipoles gradually return to their original orientation, causing a decrease in polarization.
Atomic and Molecular Structures
The atomic and molecular structures of dielectrics play a crucial role in determining their dielectric properties. Dielectrics can be classified into two main categories: polar dielectrics and non-polar dielectrics.
Polar dielectrics are materials whose molecules possess a permanent dipole moment. This means that the molecules have a separation of charges, resulting in an inherent polarity. Examples of polar dielectrics include water, alcohols, and ceramics.
Non-polar dielectrics, in contrast, are materials whose molecules do not have a permanent dipole moment. Their molecules are symmetrical and have no net charge separation. Examples of non-polar dielectrics include gases, such as nitrogen and helium, and some organic compounds.
Practical Applications
Due to their unique properties, dielectrics find widespread applications in various electrical and electronic devices and systems. Some notable applications include:
- Capacitors: Dielectrics are used as the insulating material between the plates of capacitors. Their ability to store electrical energy makes them essential for energy storage and filtering applications.
- Insulators: Dielectrics are used as insulators in electrical systems to prevent the flow of current between conductors. They ensure electrical safety and prevent short circuits.
- High-frequency circuits: Dielectrics with low dielectric loss are used in high-frequency circuits to minimize energy dissipation.
- Optical fibers: Dielectrics are used as the core material in optical fibers to guide light signals over long distances.
Dielectrics are fascinating materials that play a vital role in the field of electrical engineering. Their ability to store electrical energy, polarize under the influence of electric fields, and exhibit unique atomic and molecular structures make them indispensable for a wide range of applications. Understanding the properties and behavior of dielectrics is essential for designing and optimizing electrical devices and systems. As technology continues to advance, the exploration of novel dielectric materials with tailored properties holds immense promise for future innovations.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 85257 KB |
| Print length | : | 796 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Ed Harris
Ed Harris Brian Madison Jones
Brian Madison Jones Dennis Prager
Dennis Prager Alena Ahrens
Alena Ahrens Richard W Fatherley
Richard W Fatherley Max Weber
Max Weber Robert Dance
Robert Dance Emma Dabiri
Emma Dabiri Rachael Hale
Rachael Hale Thomas L Saaty
Thomas L Saaty Rebecca Dmytryk
Rebecca Dmytryk Eric Herrera
Eric Herrera Ben Voth
Ben Voth Gillian Price
Gillian Price Robert Goodspeed
Robert Goodspeed Heather Paxson
Heather Paxson David Albright
David Albright Patricia M Davies
Patricia M Davies Bill Adler Jr
Bill Adler Jr Paul Jellinek
Paul Jellinek
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Milton BellQuick Reference on the Psychosocial Dimensions of Cancer Symptom Management:...
Milton BellQuick Reference on the Psychosocial Dimensions of Cancer Symptom Management:...
 Felipe Blair300 Healthy And Delicious Recipes With 30 Day Meal Plan: Your Ultimate Guide...
Felipe Blair300 Healthy And Delicious Recipes With 30 Day Meal Plan: Your Ultimate Guide... Douglas PowellFollow ·10.3k
Douglas PowellFollow ·10.3k Andres CarterFollow ·15.8k
Andres CarterFollow ·15.8k Todd TurnerFollow ·15.2k
Todd TurnerFollow ·15.2k Derrick HughesFollow ·6k
Derrick HughesFollow ·6k Ian PowellFollow ·3.1k
Ian PowellFollow ·3.1k William GoldingFollow ·14.7k
William GoldingFollow ·14.7k Wayne CarterFollow ·19.6k
Wayne CarterFollow ·19.6k Leo MitchellFollow ·8.9k
Leo MitchellFollow ·8.9k

 H.G. Wells
H.G. WellsVisual Diagnosis and Care of the Patient with Special...
A Comprehensive Guide for Healthcare...

 Joshua Reed
Joshua ReedPractical Guide Towards Managing Your Emotions And...
In today's...

 Will Ward
Will WardYour Eyesight Matters: The Complete Guide to Eye Exams
Your eyesight is one of your most precious...

 Fabian Mitchell
Fabian MitchellManual For Draft Age Immigrants To Canada: Your Essential...
Embark on Your Canadian Dream with Confidence ...

 Jay Simmons
Jay SimmonsThe Ultimate Guide to Reality TV: Routledge Television...
Reality TV has...

 Nick Turner
Nick TurnerAn Idea To Go On Red Planet: Embarking on an...
Journey to the...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 85257 KB |
| Print length | : | 796 pages |